Brain science and video gaming converge in neurogaming
Published 12:00 am Tuesday, August 12, 2014
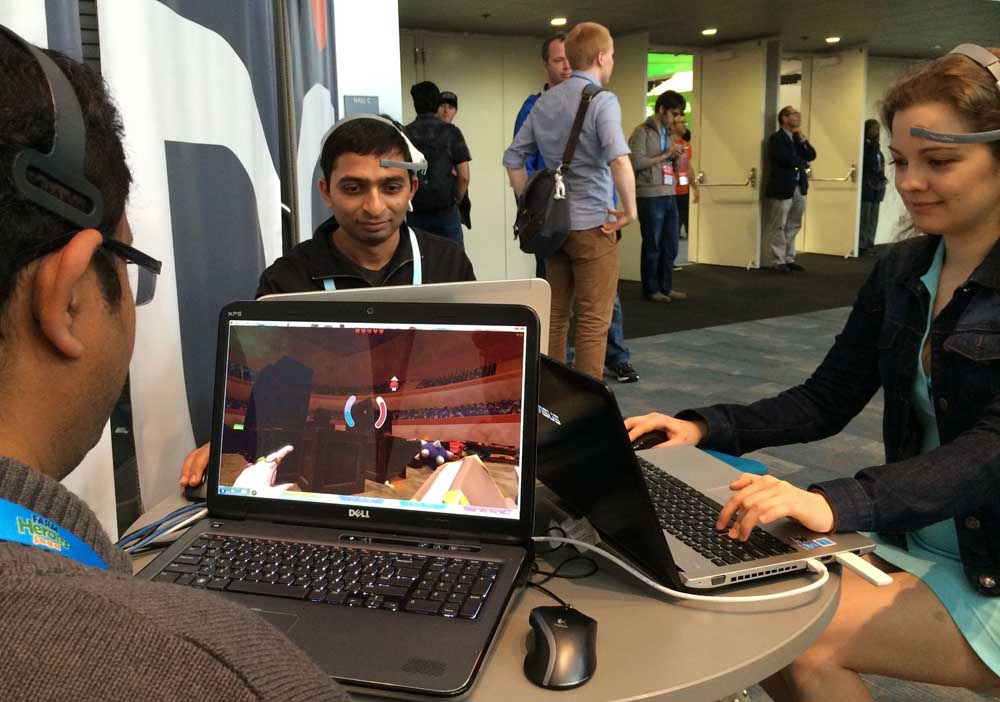
- Chris O’Brien / Los Angeles TimesThree players battle one another in “Throw Trucks With Your Mind” in March at the annual Game Developers Conference in San Francisco. In the game, players wear headsets that read their brain waves, which allows them to move objects in the game.
SAN FRANCISCO — Lat Ware pauses to straighten his jacket and organize his chaotic mind. For Ware, who has attention deficit disorder, standing in the halls of a gaming conference as people rush by can feel like being in a hurricane of humanity.
He takes a deep breath before he steps up to a passer-by to pose the question he has already asked at least 100 times today.
“Excuse me,” Ware says. “Would you like to throw trucks with your mind?”
The target’s face goes through a range of expressions, trying to formulate the appropriate response to the fantastical offer before settling on an uncertain reply.
“Um, suuuuuure …” says Natalia Veselova, who had come from Russia to attend the Game Developers Conference in March.
Ware, 29, is recruiting people to try the new video game he has developed. He leads Veselova to a table where he sits her down in front of a laptop next to other players and explains his game, “Throw Trucks With Your Mind.”
He gives her a headset that reads brain waves that indicate levels of calm and focus. Players must maximize both states of mind by concentrating on a single thought, which then allows them to pick up and hurl objects at opponents.
“It’s an ultra-violent meditative competitive game,” Ware deadpans.
For several minutes Veselova struggles to block out distractions and relax. Just when she seems ready to give up, pink and blue bars on the screen begin to spike. A swirling beam of light shoots from the hand of her avatar toward a rock in the middle of the screen that wiggles, rises and then goes flying toward an opponent, narrowly missing.
Her eyes go wide, and then a smile spreads across her face. Ware steps back with his own look of satisfaction.
The development of “Throw Trucks” places Ware on a frontier where brain science and video game developers have just begun to cross paths. The emerging field has been dubbed “neurogaming.”
Although the market for neurogaming is lightly populated now, the neuroscience industry is hoping that such games could be a catalyst that turns brain wave-reading gadgets into mainstream consumer products.
For Ware, though, the achievement is far more personal. “Throw Trucks” is the realization of an idea he first got as a teenager when he underwent an experimental treatment for ADD that involved streaming his brain waves into a computer. As he sat in a doctor’s office, he began to wonder:
“If my brain waves can be fed into a computer so I can learn to manipulate them, what else could I do with them?”
Having ADD means that Ware’s brain believes at times that every single thing is demanding his full attention. Over the years, Ware has learned to summon all of his energy to focus on one thing that actually matters at that moment.
Perversely, he can then become so obsessed with that thing, it becomes impossible for anyone or anything else to get his attention. That battle with his mind frequently leaves him exhausted and sometimes depressed.
“As a disorder, ADD does not go away,” Ware said. “You just learn the most efficient way to manage it.”
Growing up in Chapel Hill, North Carolina, Ware seemed to struggle with social relationships. After being held back one year for kindergarten, he was diagnosed with the disorder. He would try various drugs like Ritalin that would help him focus but leave him foggy and sap his creativity.
Ware’s parents kept researching other strategies, and when he was a teenager they heard about a new treatment called neurofeedback therapy. The idea is to let patients watch a computer screen that displays brain waves so they can learn to slow down or speed up their brain waves to achieve greater calm and focus.
Ware visited a clinic in Chapel Hill, where he sat in a chair facing a desk with a computer on it. A technician rubbed contact gel into his hair to improve the connection between the handful of wires that were taped to his scalp. It was messy and laborious.
He only took a few treatments, in part because it was expensive — the equipment back then cost providers thousands of dollars. But like so many other things in technology, the cost of brain wave-reading sensors has plummeted.
For his game, Ware uses a brain wave headset made by NeuroSky Inc. of San Jose, California. The gadget is roughly the same weight and shape as a headset that someone might use to make a phone call. Except instead of a microphone, a curved plastic arm rests lightly on a person’s forehead to measure brain wave activity.
No matter how “Throw Trucks With Your Mind” sells, Ware has made his mark. The game attracted the attention of Charles Huang, one of the creators of the “Guitar Hero” video game. Huang, who gets hundreds of pitches from game developers every week, said Ware stood out.
“A lot of times the most interesting products come from people with a deep personal passion for them,” Huang said. “There was something about him and his story that drew me to this. I don’t pick things like this just because of their commercial potential. I pick them because they are great products.”
Praise like this and the reception the game has received have given Ware the confidence to extend the ambition of the company he’s formed, called Crooked Tree Studios.
This success has amplified Ware’s stress, which in turn made his ADD worse. Fulfilling his grand plans will require even more energy to maintain the calm and focus he needs to resist his brain’s ever-present urge to shut down, retreat and give up.






