After reaching historic lows, hydropower generation in the Northwest expected to rise in 2025
Published 6:21 am Wednesday, May 28, 2025
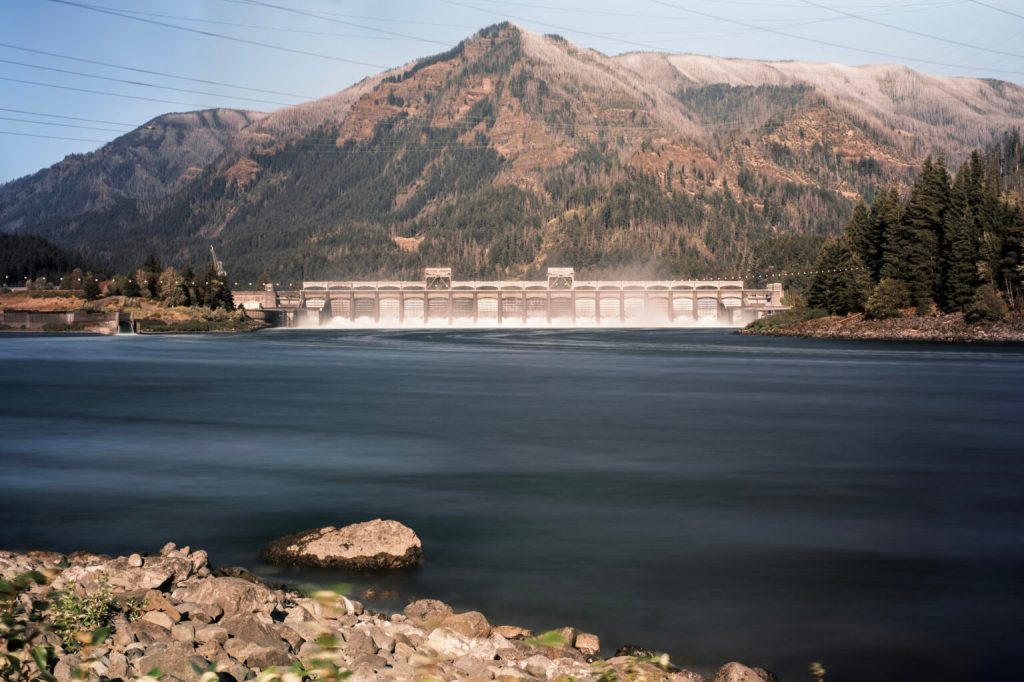

- Water flows out of the Bonneville Dam along the Columbia River between Multnomah County, Oregon and Skamania County, Washington. on Tuesday, July 23, 2024. (Jordan Gale/Oregon Capital Chronicle)
After dropping to historic levels last year due to ongoing drought and high temperatures, hydropower generated in the Northwest is expected to rise slightly this year from much needed precipitation.
Hydropower in the region is expected to increase about 17% compared to last year, a welcome boost to growing energy demand, but will still be below the 10-year average, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration.
Officials at the Energy Information Administration published their 2025 forecast on May 19, as well as annual expectations for water supplies in key river basins generating the hydroelectricity.
Overall hydropower generation in the U.S. is expected to rise 7.5% in 2025, which will also still keep overall hydropower generation below the 10-year average. Hydropower represents about 6% of the country’s electricity.
The increase in hydropower expected in 2025 is due in large part to above average precipitation in northern California, Oregon and eastern Washington during the past winter and this spring. Parts of southeast Oregon received record rainfall this spring, causing Gov. Tina Kotek in March to declare a state of emergency.
Despite the increased precipitation in some parts of the state, the Upper Columbia River Basin near Grand Coulee Dam in Washington will have a below-normal water supply this year when compared to the past 30 years, according to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s Northwest River Forecast Center. Water supply will be about normal or above normal in the southern portion of the Columbia River, which includes the Snake River Basin.
Eleven Western states produce up to 60% of the country’s hydroelectricity. Washington, California and Oregon are the three largest contributors, with dams in Oregon and Washington producing more than one-third of all U.S. hydropower. About 40% of the electricity used in Oregon comes from the region’s hydroelectric dams.
But ongoing drought, periods of low precipitation and rising summer temperatures that melt mountain snowpack too quickly have led to lower-than-usual power generating capacity at dams in the West.
Both Oregon and Washington generated 20% less hydropower in 2023 than they did in 2021, and hydropower generation in the Northwest dropped to a historic 22-year low between Oct. 2022 and Sept. 2023. Hydropower generated in 2024 was the lowest it’s been since 2010, according to the federal Energy Information Administration.
The loss in generating capacity has cost the hydropower industry billions in revenue in recent years, according to researchers from the University of Alabama. The sector lost about 300 million megawatt hours of power generation between 2003 and 2020 due to drought and low water compared with the long-term average, equating to about $28 billion in lost revenue. Half of the drop in power generation was due to drought in Oregon, Washington and California.
In Oregon, the hydroelectricity sector is estimated to have lost more than $1.5 billion in revenue over those 18 years.